引言:本文主要是对QGIS中QgsGeometry类一些算法进行说明
1、概述
QGIS API 文档:https://qgis.org/api/classQgsGeometry.html
矢量分析包含关系测试和关系计算两类。 关系测试是指元素之间有无相关关系。 关系计算是指元素之间相互关系的确切几何结果。
来源: https://blog.csdn.net/sf2gis2/article/details/41630317
1、关系测试
- 不相交disjoint:由QgsGeometry::disjoint()实现。
- 叠置overlaps:相交,但交集只是两个输入元素的一部分。由QgsGeometry::overlaps()实现
- 相交intersects:相交,比较宽泛的相交。由QgsGeometry::intersects()实现
- 包含contains:由QgsGeometry::contains()实现
- 相等equals:由QgsGeometry::equals()实现。
- 相切touches:由QgsGeometry::touches()实现。
- 内部within:与contains()相反。由QgsGeometry::within()实现。
- 经过crosses:由QgsGeometry::crosses()实现。
2、关系计算
- 并Union:指元素相互合并,相交部分从原元素中独立为单独元素。由QgsGeometry::difference()+QgsGeometry::intersection()实现。
- 交Intersection:表示两个几何图形之间共同的部分。交集多用来表示两个区域的重叠区域。由QgsGeometry::intersection()实现。注意:对于凹多边形,计算不准确。
- 差Difference:表示一个元素与另一个元素的不同之处。由QgsGeometry::difference()实现。
- 异或SymmatricDifference:表示两个元素中去除相交的部分。由QgsGeometry::symDifference()
- 融合Dissolve:多个元素合并为一个元素。由QgsGeometry::combine实现。
- 插值Interpolate:向指定的点按照一定的距离插值,形成一个新点。由由QgsGeometry::interpolate()实现。
- 缓冲区Buffer:表示向外缓冲一段距离。由QgsGeometry::buffer()实现。
- 等距线offsetCurve:表示与指定线相等距离的线。由QgsGeometry::offsetCurve()实现。
- 抽稀Simplify:将较多节点的实体减少节点。由QgsGeometry::simplify()实现。
- 加密Densify:将较少节点的实体增加节点。只能将元素点取出后逐个加密实现。
- 中心点Centroid:当前实体的中心点。由QgsGeometry::centroid()实现。
- 内部点PointOnSurface:因为多边形可能有孔,也可能有飞地,此函数保证返回一个在多边形内部的点。由QgsGeometry::pointOnSurface()实现。
- 外部多边形ConvexHull:外接多边形。由QgsGeometry::convexHull()实现。
simplify函数
QgsGeometry QgsGeometry::simplify( double tolerance ) const
{
if ( !d->geometry )
{
return QgsGeometry();
}
QgsGeos geos( d->geometry.get() );
mLastError.clear();
std::unique_ptr< QgsAbstractGeometry > simplifiedGeom( geos.simplify( tolerance, &mLastError ) );
if ( !simplifiedGeom )
{
QgsGeometry result;
result.mLastError = mLastError;
return result;
}
return QgsGeometry( std::move( simplifiedGeom ) );
}
可见是调用了qgsgeos简化算法,继续:
QgsAbstractGeometry *QgsGeos::simplify( double tolerance, QString *errorMsg ) const
{
if ( !mGeos )
{
return nullptr;
}
geos::unique_ptr geos;
try
{
geos.reset( GEOSTopologyPreserveSimplify_r( geosinit.ctxt, mGeos.get(), tolerance ) );
}
CATCH_GEOS_WITH_ERRMSG( nullptr );
return fromGeos( geos.get() ).release();
}
可见是调用了GEOSTopologyPreserveSimplify算法,再继续 http://www.postgis.net/docs/ST_SimplifyPreserveTopology.html https://geos.osgeo.org/doxygen/classgeos_1_1simplify_1_1DouglasPeuckerSimplifier.html
概要: geometry ST_SimplifyPreserveTopology(geometry geomA, float tolerance);
描述: Returns a “simplified” version of the given geometry using the Douglas-Peucker algorithm. Will avoid creating derived geometries (polygons in particular) that are invalid. Will actually do something only with (multi)lines and (multi)polygons but you can safely call it with any kind of geometry. Since simplification occurs on a object-by-object basis you can also feed a GeometryCollection to this function. Performed by the GEOS module.
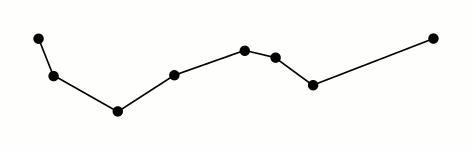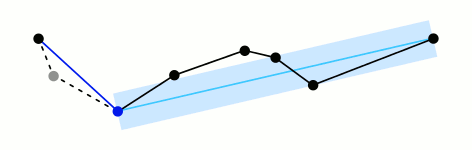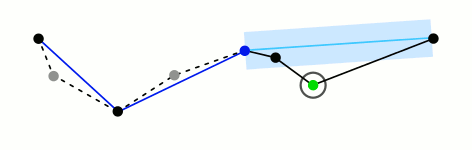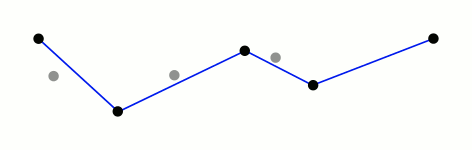
Douglas-Peucker algorithm 道格拉斯-普克算法(Douglas–Peucker algorithm,亦称为拉默-道格拉斯-普克算法、迭代适应点算法、分裂与合并算法)是将曲线近似表示为一系列点,并减少点的数量的一种算法。该算法的原始类型分别由乌尔斯·拉默(Urs Ramer)于1972年以及大卫·道格拉斯(David Douglas)和托马斯·普克(Thomas Peucker)于1973年提出,并在之后的数十年中由其他学者予以完善。
经典的Douglas-Peucker算法描述如下:
- 在曲线首尾两点A,B之间连接一条直线AB,该直线为曲线的弦;
- 得到曲线上离该直线段距离最大的点C,计算其与AB的距离d;
- 比较该距离与预先给定的阈值threshold的大小,如果小于threshold,则该直线段作为曲线的近似,该段曲线处理完毕。
- 如果距离大于阈值,则用C将曲线分为两段AC和BC,并分别对两段曲线进行1~3的处理。
- 当所有曲线都处理完毕时,依次连接各个分割点形成的折线,即可以作为曲线的近似。
buffer函数
概要 缓冲区是指以几何实体为基础,以一定的半径在周围建立起的多边形。用于与周边地物叠加,解决邻近相关性问题。
形式一
QgsGeometry buffer (double distance, int segments) const 描述 Returns a buffer region around this geometry having the given width and with a specified number of segments used to approximate curves.
形式二
QgsGeometry buffer (double distance, int segments, EndCapStyle endCapStyle, JoinStyle joinStyle, double miterLimit) const 描述 Returns a buffer region around the geometry, with additional style options.
- distance buffer distance
- segments for round joins, number of segments to approximate quarter-circle
- endCapStyle end cap style
- joinStyle join style for corners in geometry
- miterLimit limit on the miter ratio used for very sharp corners (JoinStyleMiter only)
deletePart函数
概要 bool QgsGeometry::deletePart(int partNum) Deletes part identified by the part number. 删除一部分 如果成功返回true 代码 bool QgsGeometry::deletePart( int partNum )
if ( !d->geometry ) { return false; }
if ( !isMultipart() && partNum < 1 ) { set( nullptr ); return true; }
detach(); bool ok = QgsGeometryEditUtils::deletePart( d->geometry.get(), partNum ); return ok; }
继续: ol QgsGeometryEditUtils::deletePart( QgsAbstractGeometry *geom, int partNum )
if ( !geom ) { return false; }
QgsGeometryCollection *c = qgsgeometry_cast<QgsGeometryCollection *>( geom ); if ( !c ) { return false; }
return c->removeGeometry( partNum ); }
mergeLines函数
(低版本没有哎:)说是QGIS3.0有的) 概要 QgsGeometry QgsGeometry::mergeLines ()const Returns:a LineString or MultiLineString geometry, with any connected lines joined. An empty geometry will be returned if the input geometry was not a MultiLineString geometry. 代码 QgsGeometry QgsGeometry::mergeLines() const { if ( !d->geometry ) { return QgsGeometry(); }
if ( QgsWkbTypes::flatType( d->geometry->wkbType() ) == QgsWkbTypes::LineString )
{
// special case - a single linestring was passed
return QgsGeometry( *this );
}
QgsGeos geos( d->geometry.get() );
mLastError.clear();
QgsGeometry result = geos.mergeLines( &mLastError );
result.mLastError = mLastError;
return result; }
fromPolyline函数
概要 QgsGeometry QgsGeometry::fromPolyline (const QgsPolyline & polyline)
Creates a new LineString geometry from a list of QgsPoint points. This method will respect any Z or M dimensions present in the input points. E.g. if input points are PointZ type, the resultant linestring will be a LineStringZ type.
QgsGeometry QgsGeometry::fromPolyline( const QgsPolyline &polyline ) { return QgsGeometry( qgis::make_unique< QgsLineString >( polyline ) ); }
combine函数
概要 QgsGeometry combine (const QgsGeometry &geometry) const 也就是Union操作,联合操作 Returns a geometry representing all the points in this geometry and other (a union geometry operation)
If the input is a NULL geometry, the output will also be a NULL geometry. 如果输入为空,输出为空。 If an error was encountered while creating the result, more information can be retrieved by calling error() on the returned geometry. 如果输出结果的时候出现错误,可以通过调用error()来获得更多的信息。 Note this operation is not called union since its a reserved word in C++.